How to legally purchase cryptocurrencies in the republic of Kazakhstan?
The crypto industry in Kazakhstan
The crypto industry in the Republic of Kazakhstan has received a powerful boost in growth since 2019 and continues to gain momentum nowadays. The reasons for such a rapid development of this industry are the low cost of electricity and rather liberal legislation that allows to officially engage in cryptocurrency mining. However, mining permission does not mean the free circulation of cryptocurrency.
This article provides an overview of how to acquire cryptocurrency in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Cryptocurrency in the world
In the beginning, let’s pay attention to the status of cryptocurrency in the world. The legal status of cryptocurrencies differs significantly from one jurisdiction to another, and so far there has not been one unambiguous decision.
While some countries allow the use and trading of cryptocurrencies, other countries have banned or restricted its circulation.
According to the open sources[1], the following map demonstrates the legal status of cryptocurrency in the world:
[1] Legal regime of cryptocurrencies https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Legality_of_cryptocurrency_by_country_or_territory
International Technology Park “Astana Hub”
Astana Hub residents are exempt from paying corporate income tax, personal income tax and value-added tax for the period of their residency. Another advantage of the Astana Hub is extraterritoriality, i.e. the company has the opportunity to become a resident without the obligatory binding of the office to a specific place of residence.
However, the main condition for obtaining residency at the Astana Hub is the implementation of priority activities in the field of information and communication technologies and own production’s criteria, approved by order of the Minister of Digital Development, Defense and Aerospace Industry of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated April 11, 2019 No. 37/НҚ.
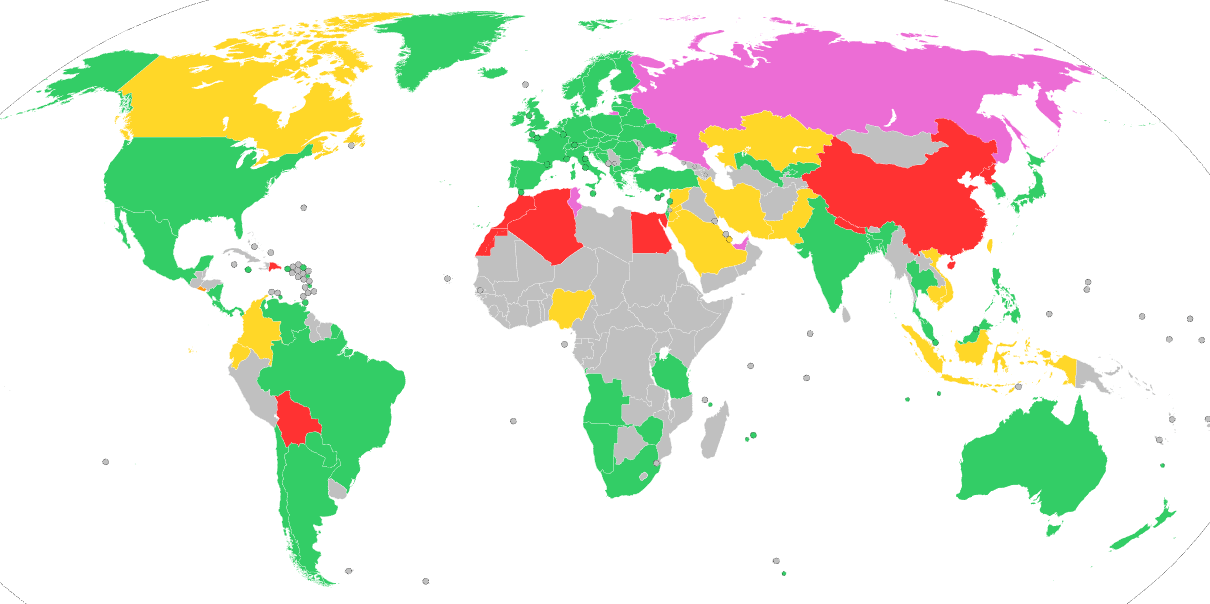

Legal Status of Bitcoin
- Accepted payment instrument
- Allowed
- Disputed status (some restrictive measures apply)
- Disputed status (outdated laws, but no outright ban)
- Prohibited (total or partial ban)
- Information not available
– As the above map shows, countries in Europe, the United States and some countries in Latin America do not interfere with the circulation of cryptocurrency and define it as a convertible decentralized virtual currency, while China, Algeria, Egypt and Morocco directly prohibit its circulation. Meanwhile, in Kazakhstan and Russia, cryptocurrency has controversial legal status, since it can be mined, but financial transactions cannot be carried out with them. In this regard, it is necessary to consider in more detail the national regulation of the cryptocurrency’s legal status.
The legal status of cryptocurrency in the Republic of Kazakhstan
In the Republic of Kazakhstan, the legal status of cryptocurrency is defined in the Civil Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated November 24, 2015 No. 418-V ZRK “On Informatization” (hereinafter referred to as the Law “On Informatization”).
Article 115 of the Civil Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan states that property benefits and rights (property) include digital asset. In other words, a digital asset, i.e. cryptocurrency is a property in the understanding of the legislator of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The Law “On Informatization” as an industry normative act contains the concept, types and features of the digital assets circulation. Thus, Article 1 of this Law defines that a digital asset is a property created in electronic digital form using cryptography and computer computing, which is not a financial instrument, as well as an electronic digital form of certification of property rights.
Considering the Civil Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Article 128-1 defines that financial instruments are money, securities, including derivative securities, derivative financial instruments and other financial instruments. Transactions with those financial instruments give rise to a financial asset of one person and a financial liability or equity instrument of another.
Moreover, paragraph 1 of Article 33-1 of the Law “On Informatization” establishes that a digital asset is not a means of payment.
In this regard, the first conclusion follows that, in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan, a digital asset (cryptocurrency) is not a payment instrument and cannot be used in financial transactions.
At the same time, paragraph 2 of Article 33-1 of the Law “On Informatization” also defines the following types of digital assets:
| Secured Digital Asset | Unsecured digital asset |
|---|---|
| Secured digital assets include a digital token and other digital assets that are a digital means of certifying property rights to goods and (or) services issued (provided) by the person who issued the secured digital asset | Unsecured digital assets include digital tokens received as a reward for participating in maintaining consensus in the blockchain, according to the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan. |
| The types of secured digital assets, as well as the list of rights certified by a digital token, are established by the person issuing a digital token in accordance with the Order of the ICRIAP RK dated October 29, 2020 No. 407/НҚ “On Approval of the Rules for the Issuance and Circulation of Secured Digital Assets”[1] | Unsecured digital assets include digital tokens received as a reward for participating in maintaining consensus in the blockchain, according to the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan. |
The main difference between secured and unsecured digital assets is the certification of property rights to the digital asset. In other words, a secured digital asset must indicate its owner and owner rights, as well as pegging to the price of a specific real asset. For example, stablecoin Tether, TrueUSD, Paxos and others can be such digital assets.
In the case of unsecured digital assets, the miner is provided with a digital token for participating in cryptocurrency mining. However, in unsecured digital assets, its owner and the rights of the owner are not indicated, and the price of such a cryptocurrency depends on many external factors. Prominent examples of unsecured digital assets are Bitcoin, Ripple, Ethereum and others.
In this regard, the Law “On Informatization” prohibits the issuance and circulation of unsecured digital assets on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, with the exception of the crypto exchange on the Astana International Financial Center platform (hereinafter referred to as the AIFC), where legal entities have the right to trade in cryptocurrency[2].
Cryptocurrency in the AIFC
As mentioned above, the Law “On Informatization” provides for an exception to the ban on the issuance and circulation of unsecured digital assets in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan. This exception is applicable under the jurisdiction of the AIFC, which allows market participants to trade cryptocurrencies.
In particular, in accordance with the Authorized Market Institution Rules (AMI), the Digital Asset Trading Facility (DATF), which is licensed by the AIFC Financial Services Regulatory Committee, is allowed to operate. (Eng. Astana Financial Services Authority, hereinafter – AFSA).
In accordance with clause 6.1 of the AMI, the following basic requirements for DATF are defined:
- transparent and non-discriminatory rules and procedures to ensure fair and orderly digital asset trading;
- objective criteria governing platform access;
- objective and transparent criteria for determining the investments that can be traded on the platform; and appropriate technological resources.
At the same time, at least once a year DATF must provide free and freely available data regarding the quality of transactions on the platform for trading digital assets. Reports should include information about the price, costs, speed and probability of execution for each individual digital asset.
Clause 6.3.1 of the AMI defines the basic requirements for the DATF regarding the admission of digital assets to trading. So, for example, a digital asset producer or his authorized representative can trade a digital asset on DATF. Also, a digital asset can be traded on the platform at the initiative of DATF itself.
However, it is worth noting that before allowing a digital asset to be traded, the DATF must ensure that the digital asset complies with the requirements of the trading rules and obtain approval from the AFSA.
Separately, we draw attention to the cybersecurity policy that needs to be developed and followed by DATF. This policy should address the following issues:
- Information Security;
- data management and classification;
- access control;
- planning and resources for business continuity and disaster recovery;
- capacity and performance planning;
- system operations and accessibility issues;
- security of systems and networks;
- system and application development and quality assurance;
- physical security and environmental control;
- confidentiality of customer data;
- management of vendors and third-party service providers; and
- response to the incident.
Simultaneously with information security, there are quantitative restrictions on clients trading in DATF. So, a client can invest in cryptocurrency only in the following amounts:
– up to $1,000 per month without proof of income;
– assets or up to (i) 10 percent of annual income, or (ii) 5 percent of total wealth for a total amount not exceeding $100,000 subject to proof of income or assets, whichever is less.
As of April 29, 2022, according to information from the AIFC Public Register, five companies are registered as DATF[3]:
| № | Company name | License number | License issue date | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ATAIX Eurasia Ltd. | AFSA-G-LA-2022-0002 | 07-04-2022 | Management of the digital assets trading platform |
| 2 | Upbit Eurasia Ltd. | AFSA-G-LA-2021-0018 | 13-07-2021 | Management of the digital assets trading platform |
| 3 | Xignal&MT Ltd. | AFSA-G-LA-2021-0016 | 29-06-2021 | Management of the digital assets trading platform |
| 4 | SD Group Ltd. | AFSA-G-LA-2021-0004 | 09-03-2021 | Working with investments as a principal, providing custody, organizing custody, managing an exchange, managing a digital asset trading platform, managing a clearing house |
| 5 | Eurasia Blockchain Fintech Group Limited | AFSA-G-LA-2019-0009 | 22-08-2019 | Provision of a depository, management of a digital assets trading platform |
An interesting example of the above companies is the Xignal&MT Ltd[4] crypto exchange. On this crypto exchange, you can create an account and trade digital assets. In particular, the following services are provided:
– exchange “Digital assets to digital assets”;
– exchange “Digital assets into fiat currency”;
– “Fiat currency to digital assets”.
This means that Xignal&MT Ltd provides its registered users with the ability to transfer payments in fiat currencies to certain third parties, including digital asset exchange, marketplace and brokerage services. Also, as of April 29, 2022, the following exchange rates for the Bitcoin cryptocurrency are provided:
| Trading pair | Minimum volume to trade | Minimum price change | Minimum order size | Maximum market order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETH/BTC | 0.001 ETH | 0.000001 BTC | 0.0001 BTC | 1,000 ETH |
| LTC/BTC | 0.01 LTC | 0.000001 BTC | 0.0001 BTC | 10,000 LTC |
| BCH/BTC | 0.001 BCH | 0.000001 BTC | 0.0001 BTC | 2,000 BC |
At the same time, a search on the Internet for methods of investing and trading through the above-mentioned other platforms registered with the AIFC did not give any results. We assume that it is possible to contact these companies in order to use their services through a request to AFSA.
In addition, it is worth highlighting the recent statement of the Agency for Regulation and Development of the Financial Market of the Republic of Kazakhstan[5], according to which it is planned to launch a pilot project for the operation of crypto exchanges at the financial center platform in cooperation with Kazakhstani banks and government agencies. In particular, this Agency developed amendments to the Decree of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated November 12, 2019 No. 188 “On approval of the Rules for the formation of a risk management and internal control system for second-tier banks, branches of non-resident banks of the Republic of Kazakhstan”, within which it is allowed to open a bank account to serve the operations of DATF clients.
Thus, it should be noted that the jurisdiction of the AIFC, as well as the Republic of Kazakhstan in general, is only at the beginning of the path to gain experience and practice in the development of the crypto industry. The question of the participation of individuals and legal entities in DATF trade remains open.
Digital tenge
In 2021, the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan implemented a Pilot Project to introduce the “digital tenge”, which is an obligation of the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan, issued in electronic form and distributed as part of a two-tier financial architecture together with market participants. In other words, a digital tenge is an additional form of the national currency tenge, which is equivalent in the market to cash and non-cash forms of tenge.
A distinctive feature of the digital tenge is the presence of a well-known and the only issuer represented by the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the establishment of an official rate. Meanwhile, stablecoins and cryptocurrencies, with similar technological approaches, have differences such as the absence of a single issuer that could guarantee the protection of the interests of citizens and their value is subject to fluctuations.
According to the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the main goals of the pilot project for 2021 were to test the viability of the digital tenge concept through the experimental confirmation of its technological feasibility of a retail platform based on distributed ledger technology.
However, as of April 29, 2022, the National Bank of the Republic of Kazakhstan has not yet made a final decision on the introduction of the digital tenge. This year, together with market participants, work is underway to expand the technological prototype of the platform, quantitative economic research and assessment of regulatory aspects.
Also, according to information from open sources[6], in the 2nd quarter of 2022, it is planned to launch the Digital Tenge Hub collaborative platform with the involvement of all interested parties. Further, in July 2022, it is planned to publish a model for assessing benefits and costs, on the basis of which a final decision on the need to introduce a digital tenge will be made by the end of this year. We assume that the current reforms will become the basis for recognizing the digital tenge as a means of payment, i.e. fiat currency[7] at the official level.
Conclusion
Summarizing this review, it should be noted that the phenomenon of cryptocurrencies in the Republic of Kazakhstan is recognized as digital assets equated to property. Digital mining is allowed on a notification basis and may soon be transferred to a licensed activity.
Moreover, the rapid development of the crypto industry may soon lead to the recognition of cryptocurrency as a means of payment in the country. The first steps in this direction have already been taken within the framework of the Astana International Financial Center. However, DATF-registered companies in the AIFC are not significantly active in attracting clients to their exchanges and, at the time of this article, have not publicly posted the rules for trading on exchanges.
Based on the above, it can be said with confidence that this article will be supplemented in the future.
____________________
If you have any questions please do not hesitate to contact us
Читать статью на русском языке
Other articles:
